What is that little secret of the fascia and its connection with Cerebral Palsy? Why is it so important to address it?

Introduction
Cerebral palsy is a neurological condition that affects a person’s motor function, muscle control, and coordination. It is often caused by damage to the developing brain during pregnancy, birth, or early childhood. While there is no known cure for cerebral palsy, recent studies suggest that fascia may play a significant role in how the condition presents and progresses.
Fascia is the connective tissue that surrounds and supports muscles, bones, and organs in the body, and it is thought that abnormal fascial tension could contribute to cerebral palsy symptoms. In this blog, we will explore the relationship between fascia and cerebral palsy and discuss how understanding this connection could lead to more effective treatments and therapies for individuals with the condition.
How might fascia be connected to cerebral palsy?
Fascia is a connective tissue that surrounds and supports muscles, bones, and organs. It is a complex network of fibers that can stretch and contract, allowing for movement and flexibility. Studies have shown that individuals with cerebral palsy may have altered fascia properties, such as increased stiffness or decreased elasticity, which can contribute to muscle stiffness and poor mobility.
Furthermore, fascia is thought to play a role in the transmission of nerve signals throughout the body. This means that changes in fascia properties may impact nerve function and potentially exacerbate neurological conditions like cerebral palsy.
Traditional treatments for cerebral palsy focus on managing symptoms and improving function through physical therapy, medication, and surgery. However, recent research suggests that there is a connection between cerebral palsy and fascia.

Recent research has challenged the traditional view that skeletal muscle in cerebral palsy (CP) is merely an end organ, and has shed light on the role of fascia in the condition. Fascia is a connective tissue that surrounds muscles, bones, and organs, and has been found to play a significant role in movement and postural control in children with CP. Fascia can become restricted and cause stiffness and pain, which can exacerbate movement difficulties in children with CP. Understanding the role of fascia in CP can offer strategies to help improve movement and postural control in affected children. [1]
In another study published in the Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions found that children with spastic cerebral palsy (a type of cerebral palsy characterized by muscle stiffness and tightness) had structural changes in their fascia, which may contribute to abnormal gait patterns [2]
Sources:
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2021.620852/full
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24989994/
What does this mean for treatment?
Understanding the potential connection between fascia and cerebral palsy can lead to new and an advanced treatment options. Currently, treatments for cerebral palsy often focus on managing symptoms such as muscle spasms, joint stiffness, and difficulty with movement. However, addressing fascial tension and restrictions may provide an additional avenue for improving motor function and reducing symptoms.
This has led to the development of innovative treatments such as PIASTM Therapy, which uses specialized Accel tool to target and release fascial restrictions in the body. By releasing tension and improving circulation, PIASTM Therapy can improve range of motion, reduce pain, and enhance overall function in individuals with cerebral palsy.
In addition to potential physical benefits, addressing fascial tension and restrictions may also improve overall well-being and quality of life for those with cerebral palsy. The fascia contains a vast network of nerve endings, which play a role in our sense of touch and proprioception (the sense of where our body is in space). By reducing fascial restrictions, individuals may experience improved sensory awareness and greater ease of movement.
What is PIASTM Therapy ?
Paediatric Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (PIASTM) is a therapeutic technique that uses specific “Accel Tool – Accelerate Healing” on children to promote mobilization of restricted tissue to increase flexibility, to increase range of motion, to reduce contractures as well as and for a management for tactile defensiveness in children diagnosed with cerebral palsy.
This technique is specifically designed by world renowned: Kanu Kaushik, Paediatric Physiotherapist.
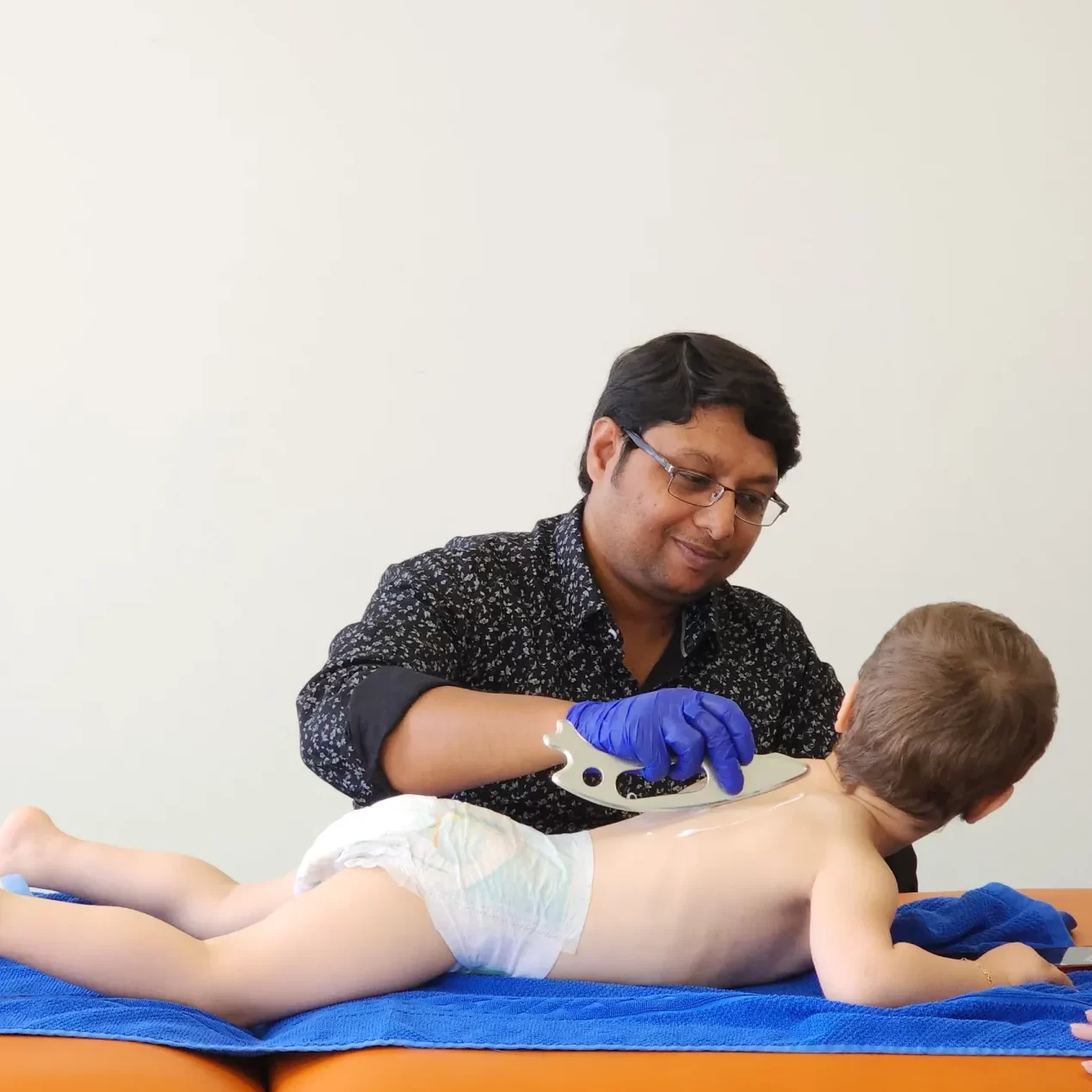
Click Below Link To Start Step by Step Process of The PIASTM Therapy Journey :
Click Below Link To See Results of the PIASTM Procedure:

En México hay algún terapeuta que maneje ese tipo de terapias
Sorry, its provided by Kanu Kaushik only in the whole world. You can connect with him to help you
Hello, I would like to know if the PIASTM course will be available in the future in the UK/Scotland or Poland.
I am Polish and live in Scotland, where I run the Physio Play clinic.
Thank you
Kind regards
Karolina